利用BIND+DLZ+MYSQL构建智能DNS
https://www.51niux.com/?id=123 已经记录了ACL和VIEW功能,前面记录的都是zone内容都记录到文件里面,当然如果域名记录比较少的话,挺合适的,因为其会会先加载到内存中,记录少又不会占太多的内容,维护也简单,响应也快。
一、介绍
1.1 智能DNS
前面已经介绍过了,就是利用BIND的view功能,不同地区联通电信等IP段都是固定的,我们有这么一个数据库,然后当用户解析一个域名的时候,根据来源的IP,跟DNS服务器内的IP库里面的数据进行批评,判断其是联通电信还是什么别线路的用户然后给用户返回对应的线路的IP地址。像万网、DNSPOD你设置的时候都可以选择来源是哪个线路然后返回哪个IP。当然如果我们可以自行架设DNS服务器,不过一般除了大公司或者CDN厂商这么干,我们一般的公司还是使用DNSPOD之类的进行域名的解析设置。
1.2 Bind-DLZ
Bind-DLZ主页:http://bind-dlz.sourceforge.net/
DLZ(Dynamically Loadable Zones)与传统的BIND9不同,BIND的不足之处:
1. BIND从文本文件中获取数据,这样容易因为编辑错误出现问题。
2. BIND需要将数据加载到内存中,如果域或者记录较多,会消耗大量的内存。
3. BIND启动时解析Zone文件,对于一个记录较多的DNS来说,会耽误更多的时间。
4. 如果近修改一条记录,那么要重新加载或者重启BIND 才能生效,那么需要时间,可能会影响客户端查询。
而Bind-dlz 即将帮你解决这些问题, 对Zone文件操作也更方便了,直接对数据库操作,可以很方便扩充及开发管理程序。
http://bind-dlz.sourceforge.net/mysql_example.html #查看在线文档链接
二、服务规划
主DNS:192.168.1.108
辅DNS:192.168.1.111
测试电信IP:192.168.1.111(CT)
测试联通IP:192.168.1.112 (CNC)
测试铁通IP:192.168.1.113 (TIETONG)
测试其他IP:192.168.1.114 (ANY)
#Bind-View返回的对应的51niux.in的子域名也是上面对应的IP地址,机器有限。
博文来自:www.51niux.com
三、安装相关环境
3.1 mysql的安装
mysql的安装就不做介绍了编译或者yum都行
3.2 bind的安装
# wget http://ftp.isc.org/isc/bind9/9.11.1/bind-9.11.1.tar.gz
#下载9最新版的bind,bind9.8之前的版本需要打patch。具体可参考DLZ官方文档,Bind9.8之后(包括9.8)的版本已经集成DLZ。
# tar zxf bind-9.11.1.tar.gz
# cd bind-9.11.1
# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/bind --with-dlz-mysql=/usr/local/mysql --enable-threads --with-openssl
# make -j 4 && make install
3.3 创建相关文件
# cd /usr/local/bind/etc/ && ../sbin/rndc-confgen >rndc.conf && tail -n10 rndc.conf | head -n9 | sed -e s/#\//g >named.conf && dig > named.root
# vim /usr/local/bind/etc/localhost.zone
$ttl 86400 @ IN SOA localhost. root.localhost. ( 2017060723 28800 14400 3600000 86400 ) IN NS localhost. 1 IN PTR localhost.
博文来自:www.51niux.com
四、配置DNS TSIG
4.1 产生加密秘钥
# mkdir //usr/local/bind/etc/keys
#cd /usr/local/bind/etc/keys
# /usr/local/bind/sbin/dnssec-keygen -a hmac-md5 -b 128 -n HOST liantong #使用dnssec-keygen function产生加密秘钥
# /usr/local/bind/sbin/dnssec-keygen -a hmac-md5 -b 128 -n HOST dianxin
# /usr/local/bind/sbin/dnssec-keygen -a hmac-md5 -b 128 -n HOST tietong
# /usr/local/bind/sbin/dnssec-keygen -a hmac-md5 -b 128 -n HOST any 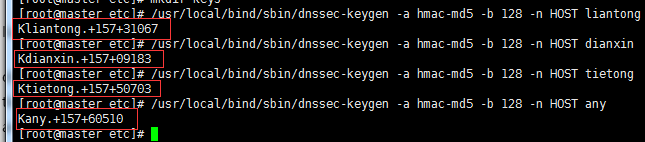
#从上图中还是很好识别的因为生成的public key和private key都带有我们设置的关键字。
# ls -l /usr/local/bind/etc/keys/
total 32 -rw------- 1 root root 47 Jun 7 23:22 Kany.+157+60510.key -rw------- 1 root root 165 Jun 7 23:22 Kany.+157+60510.private -rw------- 1 root root 51 Jun 7 23:17 Kdianxin.+157+09183.key -rw------- 1 root root 165 Jun 7 23:17 Kdianxin.+157+09183.private -rw------- 1 root root 52 Jun 7 23:15 Kliantong.+157+31067.key -rw------- 1 root root 165 Jun 7 23:15 Kliantong.+157+31067.private -rw------- 1 root root 51 Jun 7 23:20 Ktietong.+157+50703.key -rw------- 1 root root 165 Jun 7 23:20 Ktietong.+157+50703.private
4.2 配置文件named.conf文件
# cat Kliantong.+157+31067.private #查看生成的密钥文件,以联通为例
Private-key-format: v1.3 Algorithm: 157 (HMAC_MD5) Key: J6NCKmYAhP7dQsFs1XGq0A== //这是要加到named.conf文件里面去的,其他的也如此 Bits: AAA= Created: 20170607151456 Publish: 20170607151456 Activate: 20170607151456
# cat /usr/local/bind/etc/named.conf
key "rndc-key" {
algorithm hmac-md5;
secret "1sHN54rQ+LJGQlyFqcarVQ==";
};
controls {
inet 127.0.0.1 port 953
allow { 127.0.0.1; } keys { "rndc-key"; };
};
logging { //日志就记录一下请求日志方便等会查看
channel query_log {
file "/var/log/named.log" versions 3 size 100m;
severity info;
print-time yes;
print-category yes;
print-severity yes;
};
category queries {
query_log;
};
category lame-servers {
null;
};
};
options { //这里简单设置了下
directory "/usr/local/bind/etc";
pid-file "named.pid";
allow-query { any;};
recursion yes;
listen-on port 53 {
192.168.1.108;
127.0.0.1;
};
};
#TSIG-key //这里就是我们创建的四个key分别写到了对应的key名称里面
key "liantong" {
algorithm hmac-md5;
secret "J6NCKmYAhP7dQsFs1XGq0A==";
};
key "dianxin" {
algorithm hmac-md5;
secret "cfjZKMBDgtKe0ONVcrqbKQ==";
};
key "tietong" {
algorithm hmac-md5;
secret "HpM+NBoRKOOss7GWdWdNBQ==";
};
key "other_any" {
algorithm hmac-md5;
secret "YvpUSvLUgPAr1eDzWL1WMQ==";
};
#acl
acl "dnsip-list" { //设置运行我们两个dns可以访问
192.168.1.108;
192.168.1.111;
};
#acl include //设置了四个acl列表文件,都允许哪些IP访问。和一个view文件
include "/usr/local/bind/etc/liantong_acl.conf";
include "/usr/local/bind/etc/dianxin_acl.conf";
include "/usr/local/bind/etc/tietong_acl.conf";
include "/usr/local/bind/etc/any_acl.conf";
include "/usr/local/bind/etc/view.conf";4.3 配置acl文件
# cat /usr/local/bind/etc/liantong_acl.conf #这里面应该是一些网段的而非IP的形式,我这里是为了测试效果。
acl cnc{
192.168.1.112;
};
# cat /usr/local/bind/etc/dianxin_acl.conf
acl ct{
192.168.1.112;
};
# cat /usr/local/bind//etc/tietong_acl.conf
acl tietong{
192.168.1.113;
};
# cat /usr/local/bind/etc/any_acl.conf
acl otherany{
192.168.1.114;
};
4.4 创建相关数据库和表
# mysql -uroot -p123456 #我这里就用的root用户,密码是123456
mysql> create database dns_view; #创建一个dns的view库
mysql> use dns_view; #创建一个表,下面是创建表的语句
CREATE TABLE `dnstable` (
`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL auto_increment,
`zone` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`host` varchar(255) NOT NULL default '@',
`type` enum('MX','CNAME','NS','SOA','A','PTR') NOT NULL,
`data` varchar(255) default NULL,
`ttl` int(11) NOT NULL default '600',
`view` char(20) default 'DEFAULT',
`mx_priority` int(11) default NULL,
`refresh` int(11) NOT NULL default '600',
`retry` int(11) NOT NULL default '3600',
`expire` int(11) NOT NULL default '86400',
`minimum` int(11) NOT NULL default '3600',
`serial` bigint(20) NOT NULL default '2017060801',
`resp_person` varchar(64) NOT NULL default 'root.51niux.in.',
`primary_ns` varchar(64) NOT NULL default 'ns1.51niux.in.',
`data_count` int(11) NOT NULL default '0',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `type` (`type`),
KEY `host` (`host`),
KEY `zone` (`zone`)
) ENGINE=MyISAM AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=gbk;
mysql> desc dnstable; #下面是表结构截图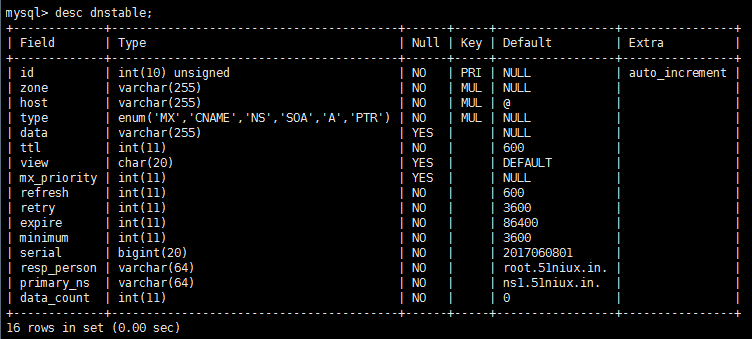
4.5 配置Bind-View-DLZ-MYSQL:
第一步:配置view.conf:
# cat /usr/local/bind/etc/view.conf
view "CNC_view" { //这是联通的view视图
match-clients { key liantong;dnsip-list;CNC;};
allow-query-cache { none; };
allow-transfer { none; };
dlz "Mysql zone" {
database "mysql //使用mysql数据库
{host=127.0.0.1 dbname=dns_view ssl=false port=3306 user=root pass=123456 } //mysql的链接方式以及连接哪个库
{select zone from dnstable where zone = '$zone$' and view = 'CNC' limit 1 } //查找语句
{select ttl, type, mx_priority, case when lower(type)='txt' then concat('\"', data,
'\"') when lower(type) = 'soa' then concat_ws(' ', data, resp_person, serial,
refresh, retry, expire, minimum) else data end as mydata from dnstable where zone
= '$zone$' and host = '$record$' and (view = 'CNC' or view = 'DEFAULT')}
{}
{select ttl, type, host, mx_priority, case when lower(type)='txt' then concat('\"',
data, '\"') else data end as mydata, resp_person, serial, refresh, retry, expire,
minimum from dnstable where zone = '$zone$' and view='CNC'}
{select zone from xfr_table where zone = '$zone$' and client = '$client$' and
view='CNC' limit 1}
{update data_count set count = count + 1 where zone ='$zone$' and view='CNC'}";
};
};
view "CT_view" { //这是电信的view视图
match-clients { key dianxin;dnsip-list;CT;};
allow-query-cache { none; };
allow-transfer { none; };
dlz "Mysql zone" {
database "mysql
{host=127.0.0.1 dbname=dns_view ssl=false port=3306 user=root pass=123456 }
{select zone from dnstable where zone = '$zone$' and view = 'CT' limit 1 }
{select ttl, type, mx_priority, case when lower(type)='txt' then concat('\"', data,
'\"') when lower(type) = 'soa' then concat_ws(' ', data, resp_person, serial,
refresh, retry, expire, minimum) else data end as mydata from dnstable where zone
= '$zone$' and host = '$record$' and (view = 'CT' or view = 'DEFAULT')}
{}
{select ttl, type, host, mx_priority, case when lower(type)='txt' then concat('\"',
data, '\"') else data end as mydata, resp_person, serial, refresh, retry, expire,
minimum from dnstable where zone = '$zone$' and view='CT'}
{select zone from xfr_table where zone = '$zone$' and client = '$client$' and
view='CT' limit 1}
{update data_count set count = count + 1 where zone ='$zone$' and view='CT'}";
};
};
view "TIETONG_view" { //这是铁通的view视图
match-clients { key tietong;dnsip-list;TIETONG;};
allow-query-cache { none; };
allow-transfer { none; };
dlz "Mysql zone" {
database "mysql
{host=127.0.0.1 dbname=dns_view ssl=false port=3306 user=root pass=123456 }
{select zone from dnstable where zone = '$zone$' and view = 'TIETONG' limit 1 }
{select ttl, type, mx_priority, case when lower(type)='txt' then concat('\"', data,
'\"') when lower(type) = 'soa' then concat_ws(' ', data, resp_person, serial,
refresh, retry, expire, minimum) else data end as mydata from dnstable where zone
= '$zone$' and host = '$record$' and (view = 'TIETONG' or view = 'DEFAULT')}
{}
{select ttl, type, host, mx_priority, case when lower(type)='txt' then concat('\"',
data, '\"') else data end as mydata, resp_person, serial, refresh, retry, expire,
minimum from dnstable where zone = '$zone$' and view='TIETONG'}
{select zone from xfr_table where zone = '$zone$' and client = '$client$' and
view='TIETONG' limit 1}
{update data_count set count = count + 1 where zone ='$zone$' and view='TIETONG'}";
};
};
view "otherany_view" { //这是其他的view视图
match-clients { key oytherany;dnsip-list;otherany;};
allow-query-cache { none; };
allow-transfer { none; };
dlz "Mysql zone" {
database "mysql
{host=127.0.0.1 dbname=dns_view ssl=false port=3306 user=root pass=123456 }
{select zone from dnstable where zone = '$zone$' and view = 'otherany' limit 1 }
{select ttl, type, mx_priority, case when lower(type)='txt' then concat('\"', data,
'\"') when lower(type) = 'soa' then concat_ws(' ', data, resp_person, serial,
refresh, retry, expire, minimum) else data end as mydata from dnstable where zone
= '$zone$' and host = '$record$' and (view = 'otherany' or view='DEFAULT')}
{}
{select ttl, type, host, mx_priority, case when lower(type)='txt' then concat('\"',
data, '\"') else data end as mydata, resp_person, serial, refresh, retry, expire,
minimum from dnstable where zone = '$zone$' and view='otherany'}
{select zone from xfr_table where zone = '$zone$' and client = '$client$' and
view='otherany' limit 1}
{update data_count set count = count + 1 where zone ='$zone$' and view='otherany'}";
};
};第二步:向数据库里面插入相关数据
插入SOA数据:
INSERT INTO `dnstable` (`zone`, `host`, `type`, `data`, `ttl`,`mx_priority`,
`refresh`, `retry`, `expire`, `minimum`, `serial`, `resp_person`, `primary_ns`,
`data_count`) VALUES
('51niux.in', '@', 'SOA', 'ns1.51niux.in.', 10, NULL, 600, 3600, 86400,
10, 2017060801, 'root.51niux.in.', 'ns1.51niux.in.', 0);插入@ NS数据:
INSERT INTO `dnstable` (`zone`, `host`, `type`, `data`) VALUES
('51niux.in', '@', 'NS', 'ns1.51niux.in.'),
('51niux.in', '@', 'NS', 'ns2.51niux.in.');插入NS A数据:
INSERT INTO `dnstable` (`zone`, `host`, `type`, `data`) VALUES
('51niux.in', 'ns1', 'A', '192.168.1.108'),
('51niux.in', 'ns2', 'A', '192.168.1.111');插入www A记录:
INSERT INTO `dnstable` (`zone`, `host`, `type`, `data`, `ttl`, `view`) VALUES
('51niux.in', 'www', 'A', '192.168.1.111', 360, 'CNC'),
('51niux.in', 'www', 'A', '192.168.1.112', 360, 'CT'),
('51niux.in', 'www', 'A', '192.168.1.113', 360, 'TIETONG'),
('51niux.in', 'www', 'A', '192.168.1.114', 360, 'OTHERANY');插入CNAME 记录:
INSERT INTO dnstable (zone,host,type,DATA,view) VALUES
('51niux.in', 'blog', 'CNAME', 'www','DEFAULT');查看一下我们现在数据库里面的数据:
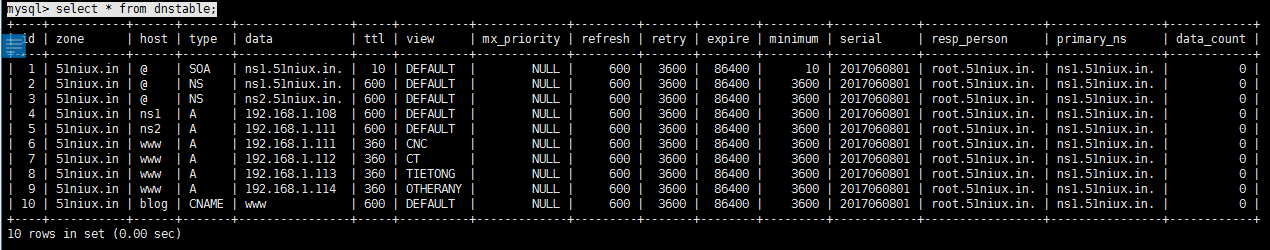
# /usr/local/bind/sbin/named-checkconf #可以用来检查配置文件有没有问题
# /usr/local/bind/sbin/named -c /usr/local/bind/etc/named.conf #启动named服务,当然也可以写个脚本来启动和关闭
# tail -f /var/log/named.log #找机器ping一下查看下日志
08-Jun-2017 01:22:02.899 queries: info: client @0x7fc7180bd540 192.168.1.111#40587 (111.1.168.192.in-addr.arpa): view CNC_view: query: 111.1.168.192.in-addr.arpa IN PTR + (192.168.1.108) 08-Jun-2017 01:22:21.476 queries: info: client @0x7fc7180bd540 192.168.1.113#41011 (www.51niux.in): view TIETONG_view: query: www.51niux.in IN A + (192.168.1.108)
#这只是展示一种思路,当你记录增多要管理的域增多之后,那种存储到文件的形式肯定不行了,必然要采取存储进数据库之类的方式。另外网上搜索还能搜到很多web管理的软件,这样就可以实现web页面管理域名记录的操作,数据库已经实现了,web的展示和操作就很好搞了。
#到这里DNS只是很小的一部分,像114.114.114.114这种对外的公网DNS服务器必然维护着一个庞大的集群以及维护着一个精确的IP库来进行智能DNS调度。DNS技术也是和CDN结合很紧密的,我们长使用CDN就会了解到我们的域名CNAME到他们提供的域名,然后CDN那边就会根据来源IP将请求发送到距离来源IP比较近的缓存服务器上面去了,这就是最简单的理解。
#到这里也只是记录了一些皮毛而已,如果真正的深入研究到DNS技术里面要学的太多太多,不仅是架构体系还要有其他方面的技术辅助还要考虑到安全性方面的问题(比如DNSFlood是DDoS的主要攻击方式,针对DNS的恶意攻击越来越多,如何规划DNS服务体系架构以适应互联网安全的需求)。
4.6 配置可以转发外网DNS请求
操作到这里呢,这台DNS服务器已经可以进行正常的我们设置好的DNS只能解析请求了,但是还存在一个问题,就是如果你想去访问www.baidu.com等之类的这些其他外网的域名解析是失败的,因为请求发过来之后去查询mysql数据库是查询不到对应的记录的,看日志也可以看到这个问题,所以呢,如果我们不仅要让我们规定好的DNS解析记录可以正常解析,又想实现其他域名解析服务的转发或者递归的话,就要再做下面的步骤。
# vim /usr/local/bind/etc/view.conf
view "otherany_view" {
match-clients {otherany;}; #如当时otherany这个acl里面的IP请求的时候,当然可以指定多个或者any
recursion yes; #开启递归
forward only; #只做转发
forwarders { 114.114.114.114;223.5.5.5; }; #转发给哪个DNS服务器
allow-query-cache {otherany; }; #这里很重要,要开启这里,不然的话会失败。
allow-recursion {otherany; }; #允许哪些IP地址可以递归
allow-transfer { none; };
....... #中间省略N行
#zone "." IN { #zone的区域要定义在这里,被这个view{}包起来,当然我们只转发,所以这里定义不定义都没什么关系,标注一下
# type hint;
# file "named.ca";
#};
};# dig>/usr/local/bind/etc/named.ca #这个可以将根的最新记录写入到named.ca这个文件中。这步可以不做,因为只做转发
#到这里重启named服务,就可以实现上网了。
# tail -f /tmp/bind_query.log #可以查询日志,已经没有报错了,解析结果也出来了。
五、扯淡
一个好的DNS服务体系应该是:智能(smart)、可扩展(Scalable)、高可用(Stable)、安全(Security)和规范化(Standard)。
智能DNS服务:
基于地理位置服务,根据用户的位置提供精确的应用或服务交付
IP智能服务检测并制止来自与恶意活动有关的IP地址进行的任何访问保护基础架构的安全性
监控外部LDNS是否可以正确解析到DNS记录
可扩展:
设备的扩展、内存级缓存响应扩展、DNS云服务扩展
高可用:
DNS集群服务,解决单点DNS服务故障。
安全:
网络层安全问题 : 网络层DOS、DDOS攻击,SYN Flooding攻击,UDP Flooding攻击,DNS request Flooding攻击、Man-In-Middle类型攻击等。
协议层安全问题:缓存投毒攻击、DNS欺诈和劫持攻击、反射类攻击、反射放大类攻击、非正常DNS请求攻击等。
系统层安全问题:基于DNS系统本身漏洞和安全隐患的攻击、缓存溢出类攻击、获取运行权限类攻击、最大查询限制攻击、区域传送限制攻击、动态更新限制攻击、递归攻击等。
规范化:
规范化部署:主DNS隐藏仅提供记录更新、所有服务均有slave提供不准改写、GSLB和BIND分离、设置RPZ、动态域名和静态域名解析分离。
规范化管理:父域监控、统计报表、突发流量日志分析、对主要运营商的LDNS周期性健康性检查与监控。
